The Los Angeles Solar Power Plant stands as a testament to the City of Angels’ commitment to clean, renewable energy. This state-of-the-art facility, one of the largest in the United States, has not only significantly contributed to the area’s power supply but has also had considerable economic and environmental impacts. This article delves into the plant’s technical details, its investment and cost, the electricity it produces, and its overall effects on the local economy and environment.
Technical Details
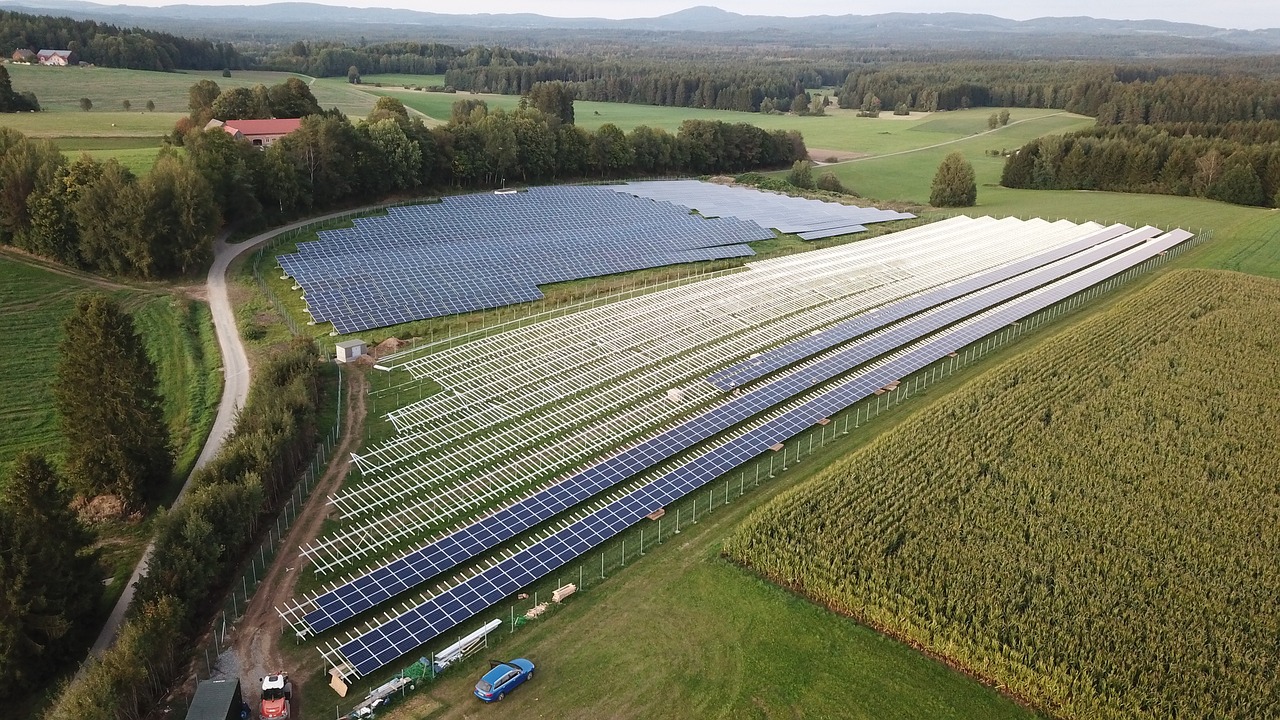
The Los Angeles Solar Power Plant is a photovoltaic (PV) plant, which converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells. The plant occupies hundreds of acres in the Mojave Desert, chosen for its ample sunlight and minimal cloud cover. With over a million solar panels, the facility boasts a capacity of 500 megawatts (MW), making it one of the largest PV plants in the country.
The Los Angeles Solar Power Plant is a grid-scale photovoltaic (PV) solar power facility. The plant sprawls over hundreds of acres and includes approximately 1.7 million solar panels, making it one of the largest solar facilities in the United States.
The solar panels are mainly composed of high-efficiency monocrystalline silicon cells, chosen for their optimal balance of cost and performance. Each panel is mounted on a motorized tracking system that allows it to follow the sun’s path across the sky, maximizing its exposure to sunlight and thus its energy output.
As for the storage system, the plant utilizes lithium-ion battery technology, widely recognized for its high energy density, long lifespan, and relative safety compared to other battery technologies. The storage capacity of the plant is rated at 400 megawatt-hours (MWh), which can help smooth out the supply of power when the sun isn’t shining, such as during the night or cloudy days. This way, the plant can ensure a constant supply of electricity to the grid.
In terms of grid connection, the plant is directly connected to the Los Angeles city grid via a high voltage transmission line. The connection includes transformers to step up the electricity produced to the appropriate voltage level for the grid, switchgear to control and protect the electrical equipment, and a substation to monitor and regulate the flow of electricity.
One of the challenges in operating a plant of this scale is maintaining the solar panels. They need to be regularly cleaned to ensure maximum efficiency, a significant task given the number of panels and the dust in the desert environment. Furthermore, occasional panel replacement is necessary due to damage from environmental conditions such as high winds or hail.
Another technical issue concerns the balance of the plant’s supply and the grid’s demand. The intermittent nature of solar power means that electricity generation can fluctuate, so the plant must work closely with the grid operator to ensure the stability of the power supply. This involves sophisticated monitoring and forecasting systems to predict the plant’s output based on weather conditions.
These are some of the main technical details and issues related to the Los Angeles Solar Power Plant. While the facility is undoubtedly complex, its operation plays a crucial role in supporting Los Angeles’s renewable energy goals.
Investment and Cost
The development of the Los Angeles Solar Power Plant was a considerable investment, costing approximately $1 billion. This capital was gathered through a combination of public and private investments, including municipal bonds and venture capital, as well as federal renewable energy subsidies. While the initial capital costs were significant, the plant’s ongoing operational costs are comparatively low, primarily consisting of maintenance for the solar panels and related infrastructure.
Electricity Production
The plant has a maximum capacity of 500 MW. Given optimal conditions, it can produce an estimated 1,300 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electricity annually, enough to power approximately 200,000 homes for a year. However, actual production varies depending on the season and weather conditions, with output typically peaking in the summer months when sunlight is most abundant.
Economic Impacts
The Los Angeles Solar Power Plant has had significant positive impacts on the local economy. The construction phase alone created thousands of jobs, and the ongoing operation and maintenance of the facility continue to support employment in the region.
Additionally, the plant has helped to stabilize electricity prices for Los Angeles residents by adding a substantial amount of renewable energy to the grid, reducing the city’s reliance on fossil fuel-based power, which is subject to price volatility. The plant also generates tax revenue for local and state governments, further contributing to the local economy.
Environmental Impacts
The environmental benefits of the Los Angeles Solar Power Plant are substantial. By producing electricity from sunlight, a renewable resource, the plant contributes to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based power plants. It’s estimated that the plant’s operations offset the emission of hundreds of thousands of tons of carbon dioxide each year.
Additionally, unlike traditional power plants, PV plants require no water for operation, an important consideration in drought-prone California. However, the plant’s location in the Mojave Desert has raised concerns about its impact on local wildlife and ecosystems, necessitating ongoing monitoring and mitigation efforts.
The Los Angeles Solar Power Plant represents a significant step forward in the transition to renewable energy. Its benefits, both economic and environmental, are considerable, but so too are the challenges it poses. Balancing the needs of clean energy production, local economies, and ecosystems will be critical as the Los Angeles region, and indeed the world, continues to embrace renewable energy sources.















+ There are no comments
Add yours